MFA regulators, insurers, and policy-makers are getting tighter on their MFA requirements, fuelled by public cyber breaches. Here's what security teams need to know about the current regulatory and insurance landscape — and how the evolution of attacks is likely to influence the future of requirements.
MFA regulators, insurers, and policy-makers are getting tighter on their MFA requirements, fuelled by public cyber breaches. Here's what security teams need to know about the current regulatory and insurance landscape — and how the evolution of attacks is likely to influence the future of requirements.
Many security leaders would confidently say they have MFA deployed everywhere. But that confidence often disappears when a breach investigation begins. The reality? MFA coverage is far from complete.
MFA is inconsistently enforced across the modern identity surface. Logins without MFA frequently slip through the cracks, exposing critical access points to business systems and data. And attackers know it — as they demonstrated best in 2024's infamous Snowflake breaches.
Regulators and insurers are catching on, too. Where MFA was once considered best practice, it’s now an expectation; implied in some frameworks, explicitly required in others, and enforced more aggressively than ever before. Whether you’re trying to meet PCI DSS, HIPAA, or GDPR requirements, the question is no longer if you have MFA, it’s where and how it’s enforced — and can you prove it?
Framework-by-framework breakdown: what they really say about MFA
MFA isn’t just a checkbox. It’s a regulatory expectation. While some frameworks spell that out clearly, others imply it in broader language. Either way, the enforcement trend is undeniable: organizations are being held accountable if MFA is missing.
Here’s how key frameworks treat MFA today:
PCI DSS v4.0 requires mandatory MFA for all non-console administrative access and remote access to cardholder environments.
HIPAA doesn’t use the term “MFA” directly, but under the Security Rule, it mandates “reasonable and appropriate safeguards,” and the absence of MFA has led to audit findings and penalties — e.g. a US children’s hospital received a $500,000 HIPAA fine for insufficient MFA.
GDPR similarly focuses on “appropriate technical measures.” In 2023, the UK’s ICO fined a UK software company £3.07 million for a breach involving missing MFA, setting a clear precedent.
NYDFS 500 is clear: MFA is required for all user access to covered systems, not just privileged accounts. MFA gaps resulted in a $3 million settlement against a financial services company, a $4.2 million dollar fine against a personal loan provider, and a $1.55 million fine against an auto insurer.
NIST SP 800-63-3 and CISA’s EO 14028 elevate the standard further, calling for phishing-resistant MFA for federal systems and contractors.
Frameworks and standards like ISO/IEC 27001, CIS Controls v8, and SOC 2 increasingly expect MFA coverage to be demonstrated during audits and certification processes.
These frameworks vary in tone and scope, but the message is consistent across the board. MFA must be enforced, not just in theory.
Insurers are scrutinising MFA gaps too
It’s not just regulators getting stricter. Insurers are building in MFA as a minimum condition of insurance coverage.
Organizations are incentivized to have MFA. Roughly 20-25% of cyber insurance premiums are dictated by the security controls in place: MFA, EDR, regular patching, etc.
After a breach, insurers bring in incident response teams to analyze what happened. Their job is to determine how the attacker got in and whether the controls you claimed to have were actually in place. If the entry point had no effective MFA and your policy attested that it did, the insurer may treat that as misrepresentation.
If your self-attested MFA coverage doesn’t hold up under investigation, your provider may not be required to pay, and you’re left footing the bill for IR, recovery, legal fees, and business disruption.
Case study: City of Hamilton, Ontario
The Canadian city of Hamilton, Ontario fell victim to a ransomware attack in February 2024. Attackers disabled nearly 80% of the city’s network and demanded a ransom of roughly $18.5 million in exchange for a decryption tool to unscramble the data.
They attempted to claim $5 million under their cyber insurance policy. After more than a year of dispute, the claim was denied because of MFA gaps — a condition of the coverage. Taxpayers were left to foot the $18.3 million bill, including cleanup, rebuild, and one-time consultancy fees.
The future of compliance will be driven by cyber attacks
The direction of travel is consistent: frameworks are getting stricter, auditors are getting more technical, and enforcement is starting to hit data processors as well as controllers.
But there’s more to it than that. In-the-wild breaches are exposing just how much business IT has evolved — and where security controls haven’t kept up.
With the SaaS-ification of enterprise IT, core business systems aren’t locally deployed and centrally managed in the way they used to be. Instead, they’re logged into over the internet, via a web browser.
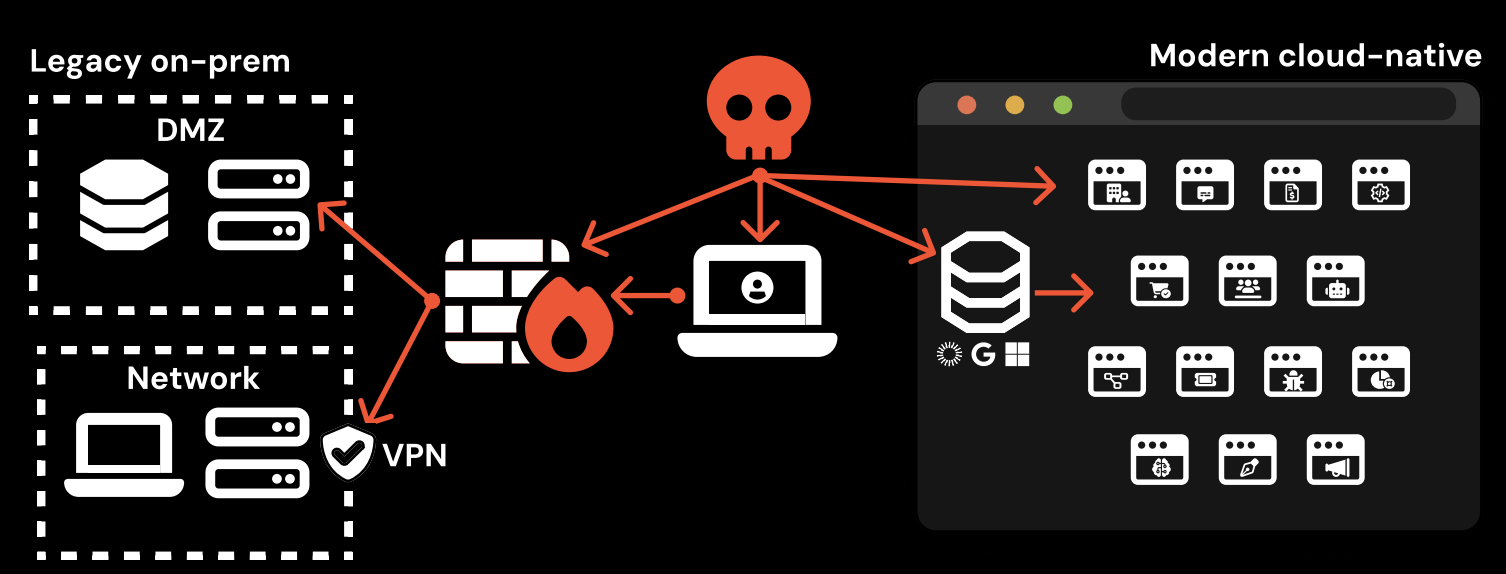
So it’s not surprising that modern attackers are now targeting these apps directly. The most logical way to do this is by targeting users of those apps via identities — the vehicle by which apps are accessed and used.
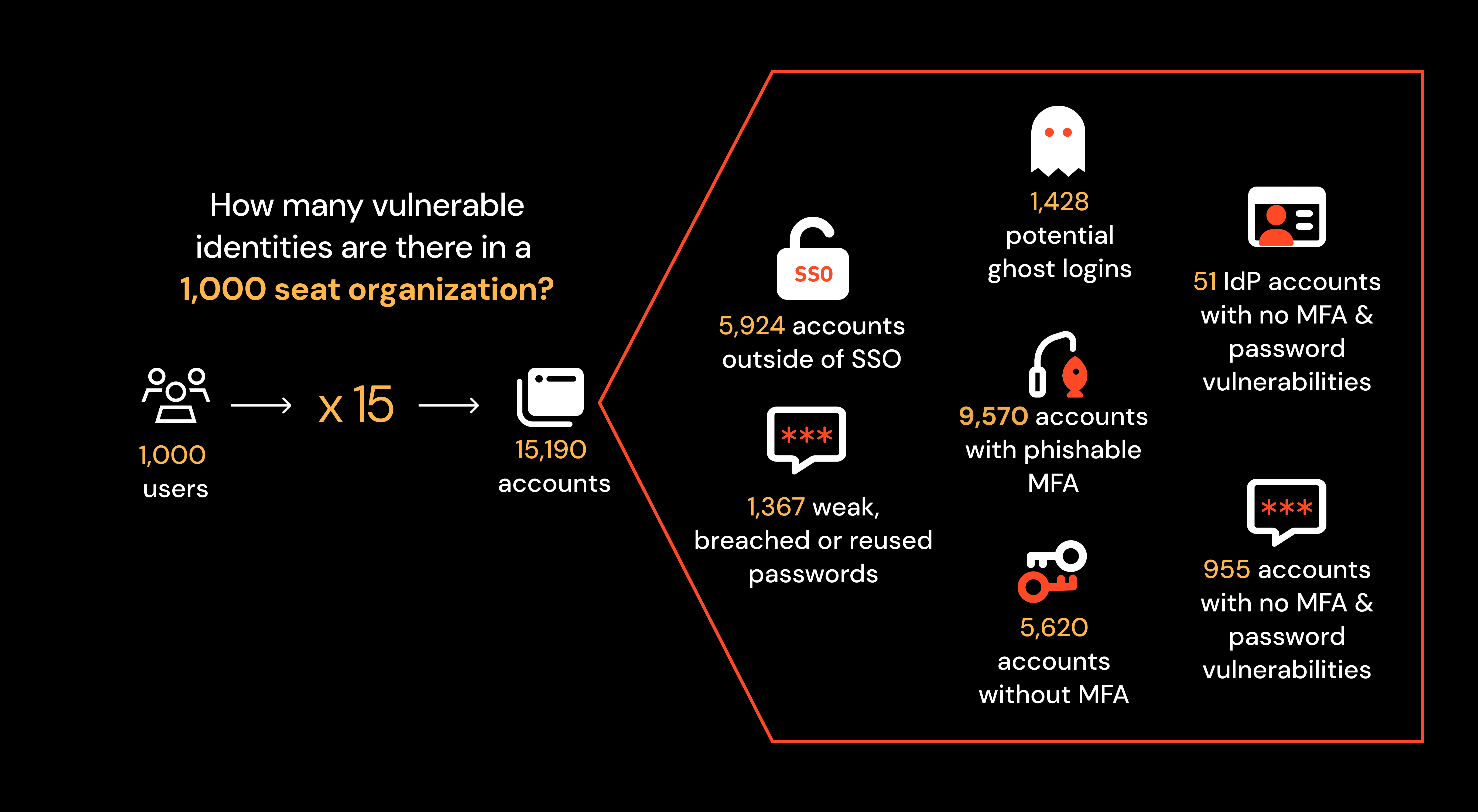
Sitting outside the typical security control boundary, it’s no surprise that this has become the soft underbelly in the crosshairs of attackers. Organizations are dealing with a vast and vulnerable attack surface consisting of hundreds of applications, with thousands of accounts spread across the app estate. 2 in 5 of these accounts are missing MFA, and many also have a password vulnerability (such as appearing in a password breach or compromised credential feed) that means they’re sitting ducks for an attacker, waiting to be exploited.
Due to SaaS blind-spots, 2 in 5 accounts are missing MFA.
What security teams can do about it
Achieve complete MFA visibility and remediate gaps with Push Security
You can’t enforce identity policy if you can’t see where it breaks. Push gives you live, browser-based insight into how users actually authenticate – what apps they access, how they log in, and where protections like MFA fall short. Because Push runs natively in the browser, you get full coverage and built-in guardrails, without relying on app integrations, enabling you to:
Understand how identities are really used across apps
Catch misconfigurations, missing MFA, and accounts using vulnerable passwords
Guide users to fix issues before they become incidents
Prepare your organization for the new world of browser-based attacks
As attacks continue to evolve, we can expect regulators, insurers, and policy-makers to follow.
Attacks that target users in their web browsers have seen an unprecedented rise in recent years, exploiting the biggest security blind-spot in the enterprise security stack.

Push Security’s browser-based security platform provides comprehensive detection and response capabilities against the leading cause of breaches. Push blocks browser-based attacks like AiTM phishing, credential stuffing, password spraying and session hijacking using stolen session tokens. You can also use Push to find and fix vulnerabilities across the apps that your employees use, like ghost logins, SSO coverage gaps, MFA gaps, vulnerable passwords, risky OAuth integrations, and more to harden your identity attack surface.
To learn more about Push, check out our latest product overview or book some time with one of our team for a live demo.
