It takes less than two minutes to check all your Office 365 or Google Workspace mailboxes.
Case study: Business Email Compromise (BEC) attack nearly cost us millions
An interesting BEC example. After attackers gained access to a senior employee's email account they began their Business Email Compromise (BEC) attack. They created a mail rule that forwarded all payment emails to another address and then followed up with an email changing the banking details. This nearly resulted in millions lost.
An interesting BEC example. After attackers gained access to a senior employee's email account they began their Business Email Compromise (BEC) attack. They created a mail rule that forwarded all payment emails to another address and then followed up with an email changing the banking details. This nearly resulted in millions lost.
The following is a personal account from the owner of an engineering consulting and projects company of how a Business Email Compromise (BEC) attack played out against his company, almost costing them millions.
It started with a phone call from one of our customers. They wanted to make a payment to us and asked to confirm that our banking details had changed. They had not. Our customer explained they had received another email from us after our original invoice, stating that our banking details had changed.
So many questions ran through my mind. I assured them our details had not changed and asked them to send me the email that they had received.
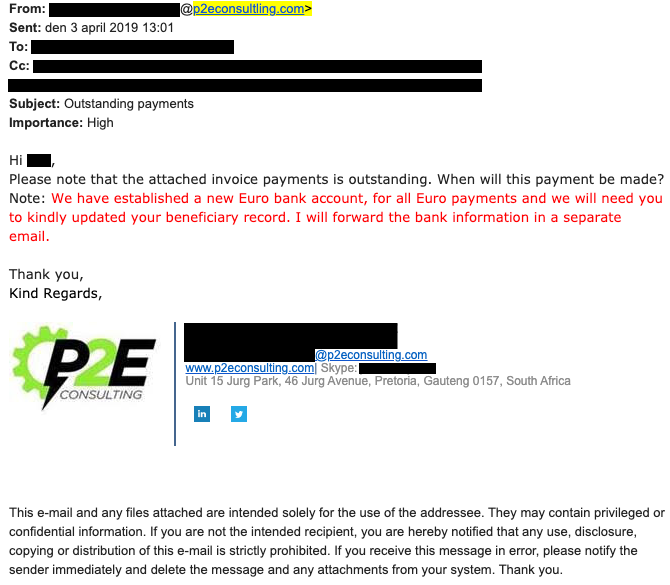
There it was. It even had our company logo and signature at the bottom.
We didn't know how the attacker got access to that email account and we assumed they were logging in and reading emails. So we changed the password on the affected email account and moved on.
A day later, the attacker followed up again with the customer and we got another phone call. After having a really difficult conversation, we had to dig deeper and find out what was going on. So we contacted our IT provider and launched an investigation.
We found that the email we sent containing the invoice was also forwarded to an external Gmail address. The attacker had also registered a visually similar domain name and cloned the look and feel of our emails to reply to our customers and trick them into believing it was from us. This 1-letter difference in the domain is highlighted in the image above.
The primary culprit behind the forwarding of the message was then discovered. A mail rule had been created that forwarded emails with the word "payment" (among others) in the subject.
Some senior employees had received phishing emails a few days prior to this incident taking place. The email took them to a fake Microsoft login page and unfortunately one of them entered their password.
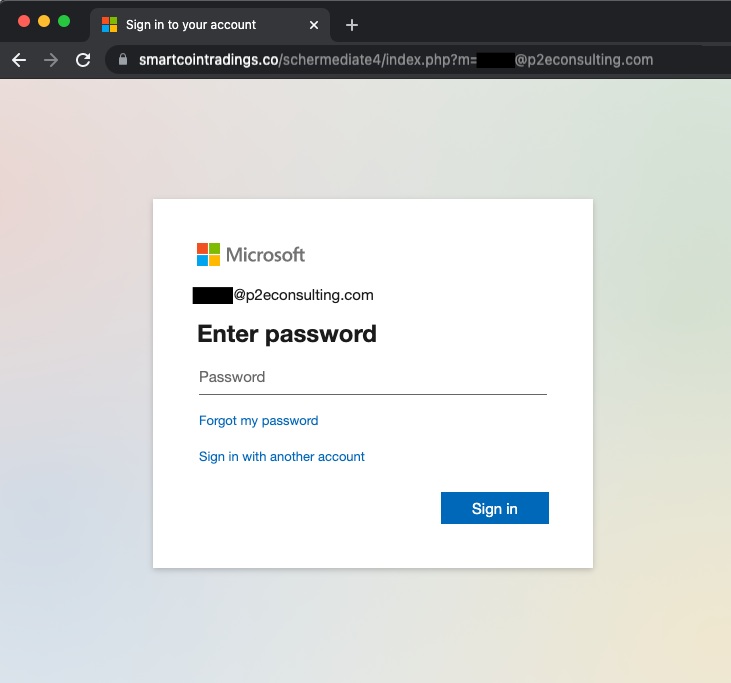
This stolen password was used to log in and set up the forwarding rule. This closed the loop and we understood what happened fully.
We learned a lot from the incident (and aged a few years!) and the main recommendations from our IT provider were to delete the mail rule, change the password again and enable MFA on all our email accounts. Had this customer paid this invoice without questioning the change of details, we would have lost millions.

